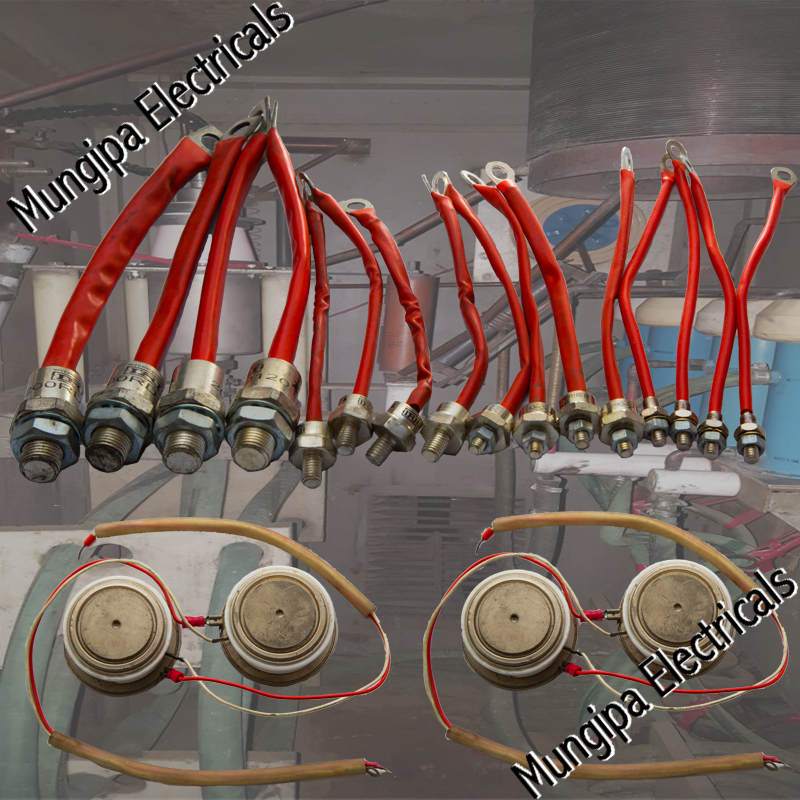
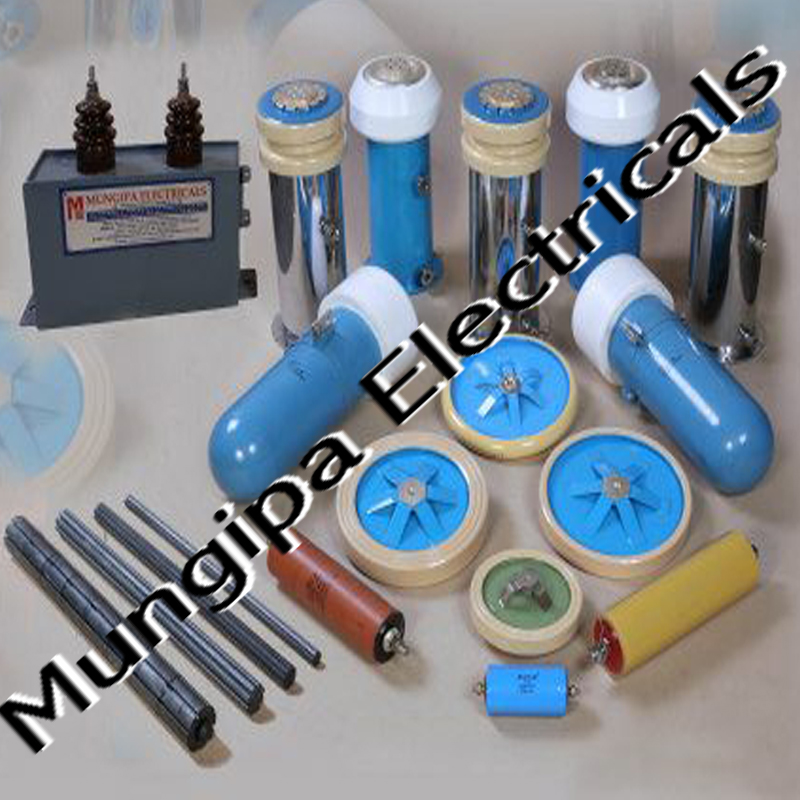
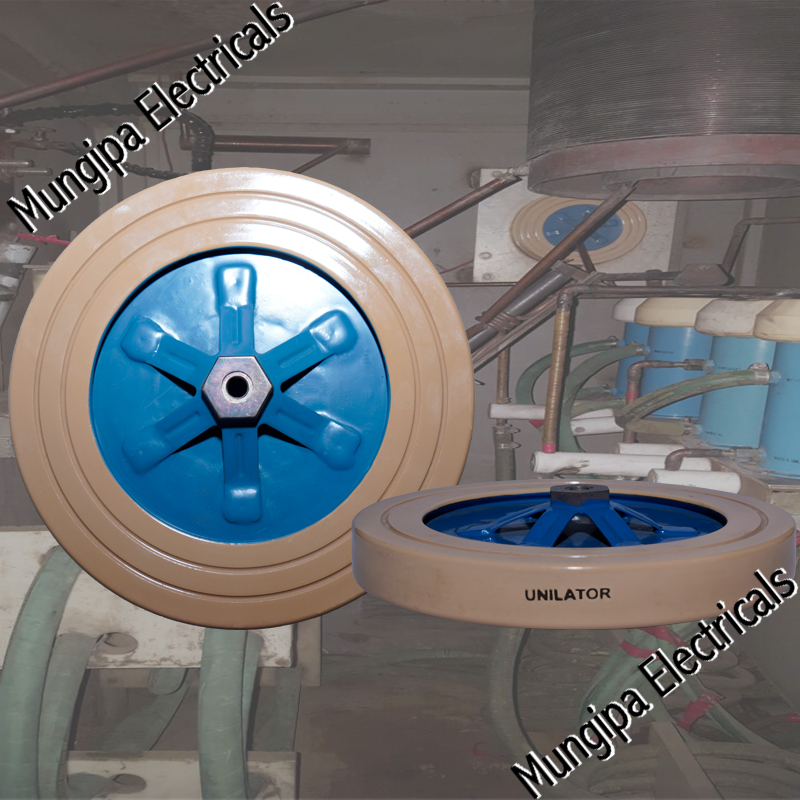
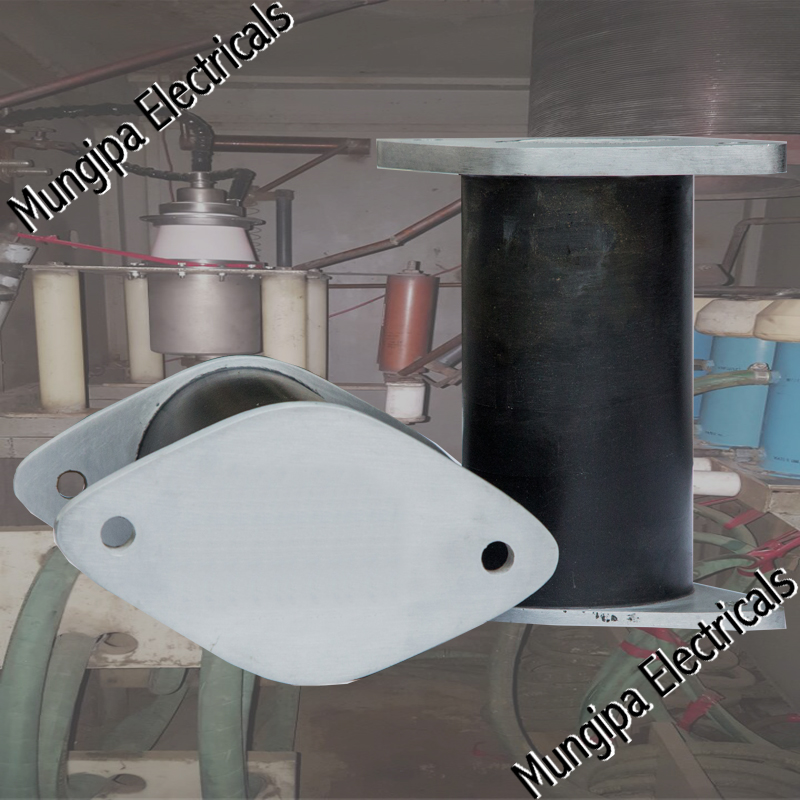
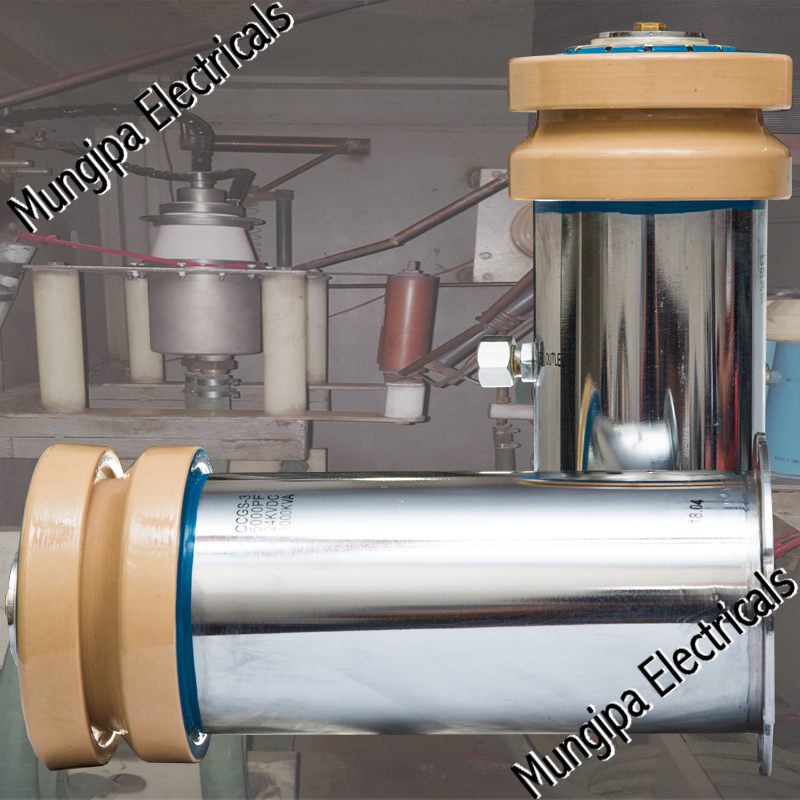
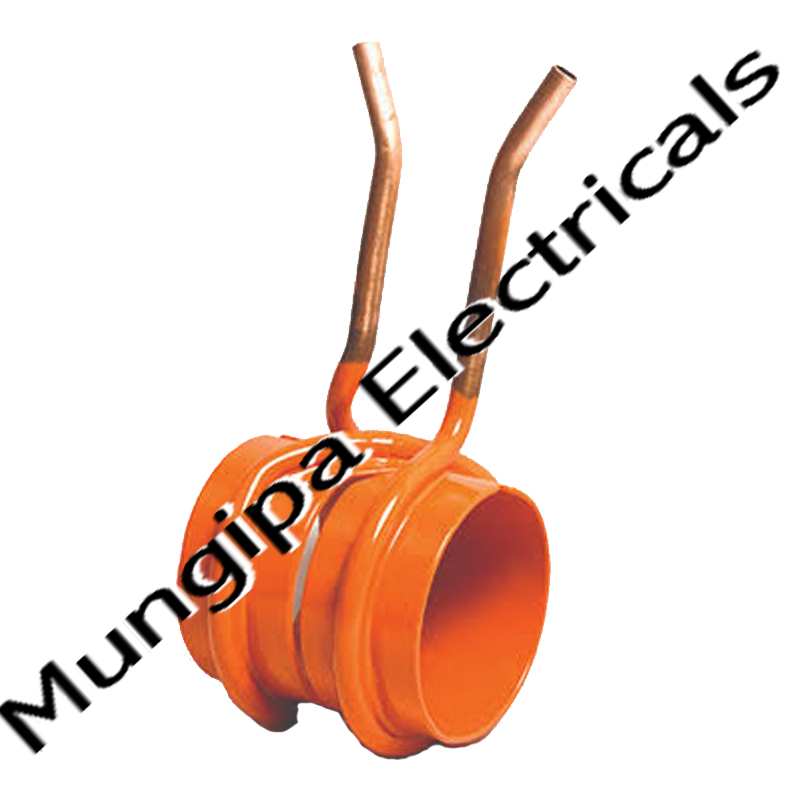
DIODES / THYRISTORS
A diode is an electrical device allowing current to move through it in one direction with far greater ease than in the other. The most common kind of diode in modern circuit design is the semiconductor diode, although other diode technologies exist. A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction; it has low resistance in one direction, and high resistance in the other
A Thyristor is a four-layered semiconductor rectifier in which the flow of current between two electrodes is triggered by a signal at a third electrode. A thyristor usually has three electrodes: an anode, a cathode, and a gate. A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch, conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed.